The Gemini constellation is one of the most recognizable and iconic constellations in the night sky. It is visible from both hemispheres and has been known and named by various civilizations for thousands of years. The Gemini constellation is located between Taurus and Cancer and contains many notable celestial objects, including stars, clusters, and nebulae. In this article, we will delve into the history, mythology, and fascinating features of the Gemini constellation.
History
The Gemini constellation has been known and named by various civilizations for thousands of years. The ancient Greeks named the constellation after the twins Castor and Pollux, who were the sons of Zeus and Leda. The twins were known for their incredible bond, and their story has been told in many cultures throughout history.
Mythology
According to Greek mythology, Castor and Pollux were the sons of Zeus and Leda. Castor was the mortal son of Tyndareus, the king of Sparta, while Pollux was the immortal son of Zeus. The twins were known for their exceptional bond, and their story has been told in many cultures throughout history. They were known for their bravery and were considered the patron saints of sailors. In the sky, the twins are depicted holding hands.
Notable Celestial Objects
The Gemini constellation contains many notable celestial objects, including stars, clusters, and nebulae. One of the most famous objects is the Eskimo Nebula, also known as NGC 2392. The nebula is located approximately 5,000 light-years away and is known for its distinctive shape, which resembles a face inside a furry parka. Another famous object is the open cluster M35, which contains over 120 stars and is located approximately 2,800 light-years away.
Finding Gemini
To find the Gemini constellation in the night sky, you need to look for it during the winter months if you are in the Northern Hemisphere or during the summer months if you are in the Southern Hemisphere.
If you are in the Northern Hemisphere, look towards the east-southeast sky at around 8 pm local time in early January. You should be able to see the two bright stars, Castor and Pollux, which represent the twin brothers. They are located in the constellation’s “heads.”
If you are in the Southern Hemisphere, look towards the north-northwest sky at around 10 pm local time in early June. You should be able to see the same two bright stars, Castor and Pollux, which represent the twin brothers. They are also located in the constellation’s “heads.”
Once you have identified Castor and Pollux, you can trace the rest of the constellation’s outline. The twins are depicted holding hands, with their bodies forming the constellation’s shape. The constellation also includes other notable stars and objects, such as the Eskimo Nebula and M35 open cluster.
Remember that light pollution can make it difficult to see stars and constellations, so try to find a dark area away from city lights for the best viewing experience. Additionally, using a star chart or a stargazing app on your smartphone can be helpful in identifying and locating the Gemini constellation.
Castor and Pollux
Castor and Pollux are two bright stars located in the Gemini constellation, which is named after the twin brothers from Greek mythology. The stars are among the brightest in the night sky and are easily visible with the naked eye.
Castor is the second brightest star in Gemini and is a multiple star system consisting of at least six stars. It is located approximately 51 light-years away from Earth and has a magnitude of 1.58, making it one of the brightest stars in the sky.
Pollux is the brightest star in Gemini and is a giant star located approximately 33.7 light-years away from Earth. It has a magnitude of 1.14, making it the 17th brightest star in the sky. Pollux is a red giant star and is about 10 times larger than our Sun.
According to Greek mythology, Castor and Pollux were the twin sons of Zeus and Leda. Castor was mortal, while Pollux was immortal. The twins were known for their exceptional bond, and their story has been told in many cultures throughout history. They were considered the patron saints of sailors and were known for their bravery.
In the sky, Castor and Pollux are depicted holding hands, forming the heads of the twins in the Gemini constellation. The stars have been used for navigation by sailors for centuries, and they continue to be a source of inspiration and wonder for stargazers around the world.
Other stars in Gemini
In addition to Castor and Pollux, the Gemini constellation contains many other notable stars. Here are a few examples:
- Alhena: Alhena is the third brightest star in the Gemini constellation and is located approximately 105 light-years away from Earth. It is a blue-white subgiant star with a magnitude of 1.93.
- Wasat: Wasat is a binary star system located approximately 59 light-years away from Earth. It consists of two stars orbiting around a common centre of mass, and it has a magnitude of 3.52.
- Mebsuta: Mebsuta is a multiple star system located approximately 900 light-years away from Earth. It consists of at least three stars and has a magnitude of 3.06.
- Tejat: Tejat is a binary star system located approximately 230 light-years away from Earth. It consists of two stars, with the primary star being a blue-white subgiant and the secondary star being a red dwarf.
- Mekbuda: Mekbuda is a red supergiant star located approximately 1,250 light-years away from Earth. It has a magnitude of 3.68 and is one of the largest known stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
These stars, along with Castor and Pollux, make the Gemini constellation a fascinating area of the sky to explore for stargazers and astronomers alike.
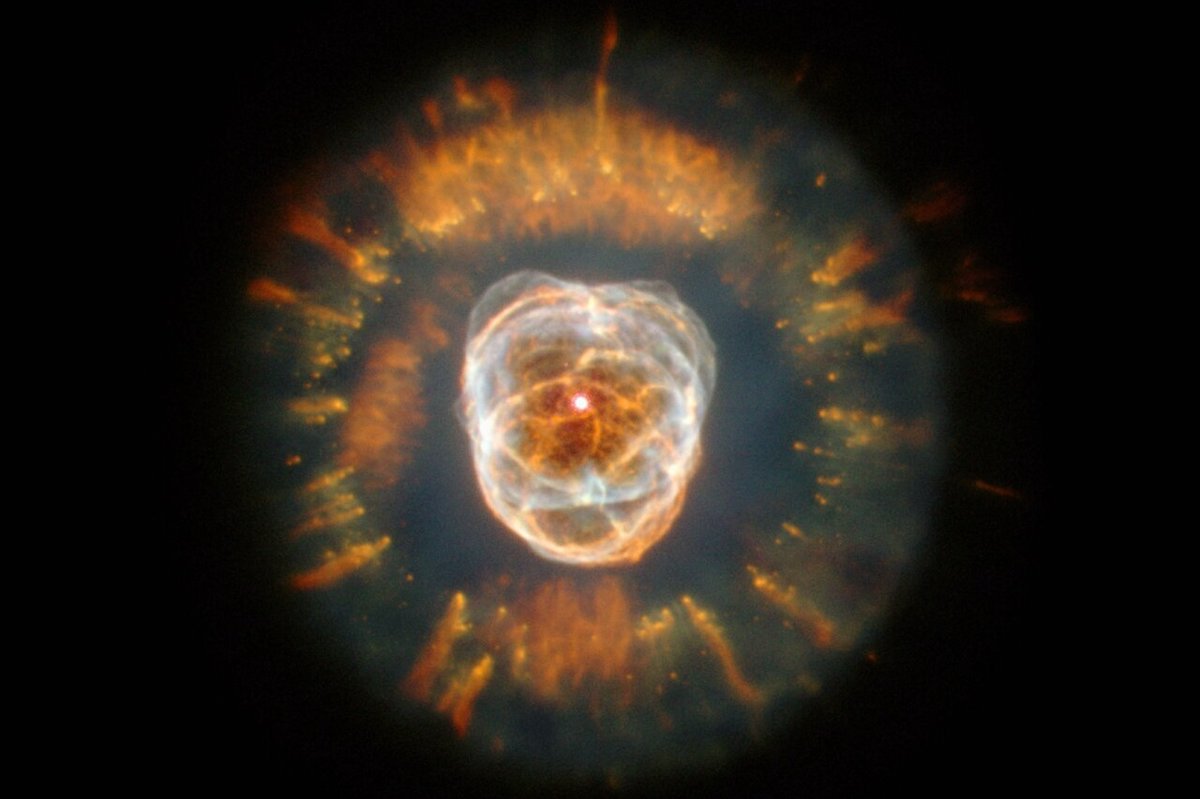
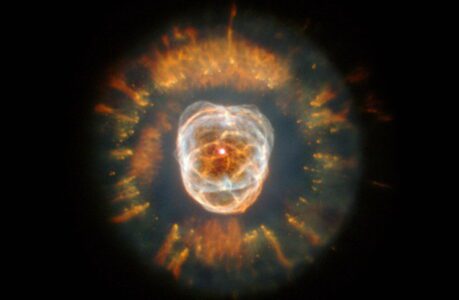
Eskimo Nebula
The Eskimo Nebula, also known as NGC 2392, is a planetary nebula located in the Gemini constellation. It is a popular object for stargazers and astronomers alike, and it has been photographed by many space observatories, including the Hubble Space Telescope.
The Eskimo Nebula was first discovered in 1787 by William Herschel, a famous astronomer. It is located approximately 2,870 light-years away from Earth and has a diameter of about 0.6 light-years. The nebula gets its name from its resemblance to a face inside a furry parka, which is reminiscent of an Eskimo or Inuit.
The Eskimo Nebula is formed by the outer layers of a dying star that have been expelled into space. The central star of the nebula is a white dwarf, which is the remnant of the original star that has collapsed into a small, dense object. The nebula’s outer layers are ionized by the intense ultraviolet radiation from the central star, which causes them to glow.
The Eskimo Nebula is a beautiful object to observe through a telescope. Its central star is visible as a bright point of light, surrounded by a disk of gas and dust. The nebula’s outer layers are visible as a delicate, intricate pattern of filaments and knots, which are the result of the star’s winds interacting with the surrounding gas.
The Eskimo Nebula is an excellent example of a planetary nebula and is an important object for studying the later stages of a star’s life. It is also a reminder of the beauty and complexity of the universe around us, and it inspires wonder and awe in those who observe it.
M35 Open Cluster
The M35 Open Cluster is a beautiful and fascinating object located in the Gemini constellation. It is one of the most prominent open clusters in the night sky and is a popular target for stargazers and astronomers.
The M35 Open Cluster is located approximately 2,800 light-years away from Earth and has an estimated age of around 150 million years. It contains over 120 stars and has a diameter of about 24 light-years. The cluster is relatively young, and its stars are still in the process of forming, making it an important object for studying star formation.
The M35 Open Cluster is a beautiful sight to behold through a telescope. Its stars are arranged in a loose, scattered pattern, with some of the brightest stars forming a distinctive “V” shape. The cluster’s stars are mostly blue-white and are located in the disk of the Milky Way galaxy, which gives them a stunning backdrop of faint, distant stars and dust clouds.
In addition to its beauty, the M35 Open Cluster is an important object for studying the properties of stars. The cluster contains stars of different masses and ages, which allows astronomers to study the relationship between a star’s properties and its evolution. The M35 Open Cluster has also been used to study the distribution of interstellar dust and gas in our galaxy.
Overall, the M35 Open Cluster is a fascinating object to explore for both amateur and professional astronomers. Its beauty and scientific significance make it an important object for studying star formation and evolution, and it continues to inspire wonder and awe in those who observe it.
Gemini
The Gemini constellation has a rich history and mythology, and its notable celestial objects make it a fascinating sight to behold. Its prominence in the night sky has made it a source of wonder and inspiration for humans throughout history. Whether you’re a seasoned astronomer or a casual stargazer, the Gemini constellation is definitely worth exploring.