The Oort Cloud is a mysterious and enigmatic region of space that is believed to exist at the outer reaches of our solar system. Named after the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, who first proposed its existence in 1950, the Oort Cloud is a vast expanse of icy bodies that is thought to contain billions of comets and other objects. Despite being one of the most intriguing and least understood features of our solar system, the Oort Cloud remains largely unexplored and shrouded in mystery. In this article, we will delve into the mysteries and marvels of the Oort Cloud, and explore what makes it such an exciting area of study for astronomers and space enthusiasts alike.
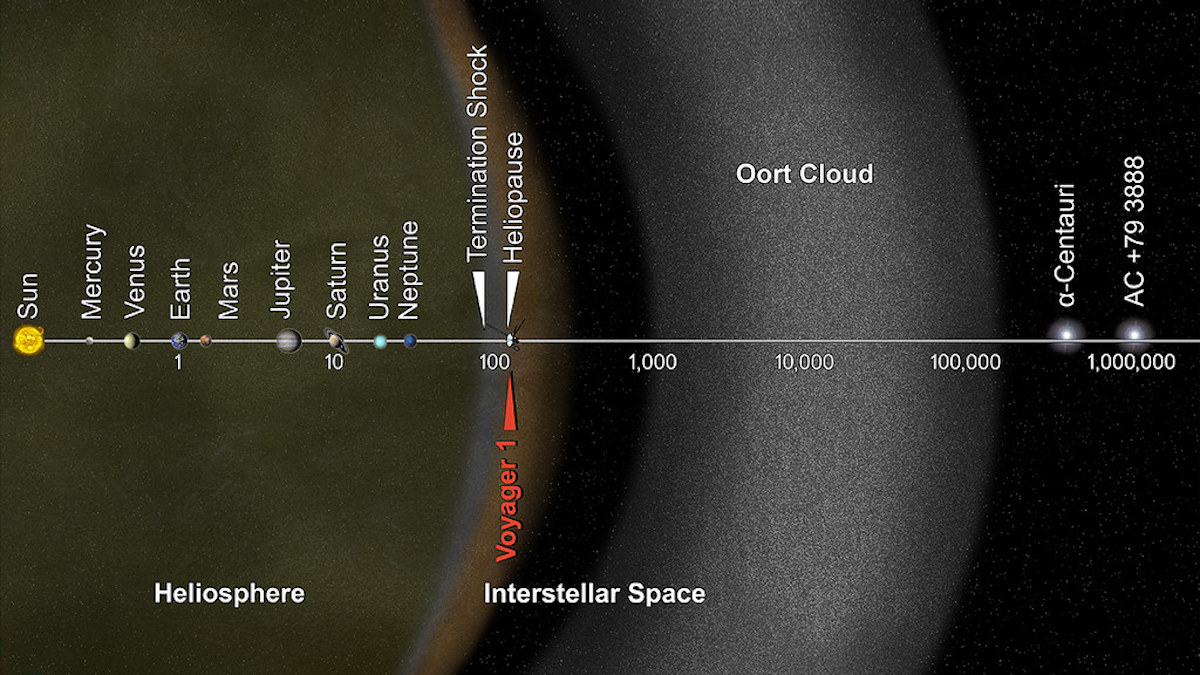
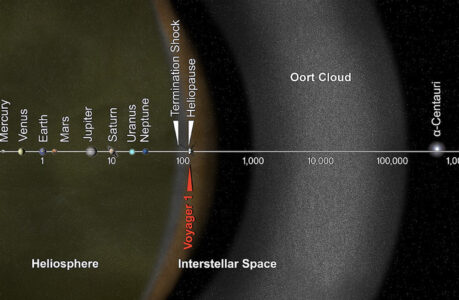
The Oort Cloud is believed to be a spherical shell that surrounds the outer edges of our solar system, extending out to a distance of up to 100,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun. To put this into perspective, one AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun, which is approximately 93 million miles. Therefore, the Oort Cloud is located well beyond the orbit of Neptune, the outermost planet in our solar system, and is thought to be the source of long-period comets that occasionally venture into the inner solar system.
The exact nature and composition of the Oort Cloud remains uncertain, but it is generally believed to be made up of a mixture of ice, rock, and other materials. The objects within the Oort Cloud are thought to be remnants from the early days of our solar system, when the planets and other bodies were still forming. As such, studying the Oort Cloud can provide important insights into the history and evolution of our solar system.
Despite its importance, the Oort Cloud has proved to be a difficult area to study, due to its vast distance from the Sun and the fact that it is composed of small, relatively dim objects. Nonetheless, astronomers have developed various methods for detecting and studying the Oort Cloud, including indirect observations of its effects on comets and other objects, as well as direct observations of individual objects that may have originated from the Oort Cloud.
One of the most significant discoveries in the study of the Oort Cloud came in 1983, when the astronomer Jan Hendrik Oort himself was still alive. In that year, the famous astronomer Gerry Neugebauer and his team discovered a large object orbiting beyond Neptune, which they named Pluto. Although Pluto is no longer considered a planet, its discovery was significant as it provided the first direct evidence of a large object beyond the orbit of Neptune, and helped to confirm the existence of the Oort Cloud.
Since then, numerous other objects have been discovered in the outer reaches of our solar system, including many that are believed to have originated from the Oort Cloud. These objects, known as trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs), include dwarf planets such as Eris, Makemake, and Haumea, as well as smaller bodies like Sedna and 2012 VP113. Studying the properties and orbits of these objects can provide valuable insights into the structure and composition of the Oort Cloud.
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Oort Cloud is its potential role in the formation and evolution of life in the universe. Some scientists have suggested that the Oort Cloud may have been responsible for bringing water and other organic compounds to Earth during its early history, which could have played a crucial role in the development of life on our planet. The Oort Cloud may also be home to undiscovered objects that could hold clues to the origins of life in the universe, making it a prime target for future exploration and study.
In recent years, there have been several proposed missions to explore the Oort Cloud and study its composition and structure. One such mission is the Oort Cloud Express, which was proposed by a group of scientists and engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The mission would involve sending a spacecraft to the Oort Cloud, where it would collect samples of comet and asteroid material, and return them to Earth for analysis.
Another proposed mission, called the FOCAL mission, would involve placing a telescope at a distance of 550 AU from the Sun, where it would be able to observe objects in the Oort Cloud with unprecedented detail. The mission would provide valuable insights into the properties and origins of the objects in the Oort Cloud, and could help to shed light on the mysteries of our solar system’s early history.
Despite the many mysteries and marvels of the Oort Cloud, much remains unknown about this enigmatic region of space. However, as technology and scientific understanding continue to advance, we are sure to uncover new and exciting discoveries about this cosmic wonderland beyond our solar system. Whether studying the origins of life or unlocking the secrets of our solar system’s early history, the Oort Cloud is a treasure trove of scientific knowledge and wonder that is sure to capture the imagination of scientists and space enthusiasts for generations to come.
Can you see the Oort cloud from earth?
The Oort Cloud cannot be directly observed from Earth as it is located at a distance of up to 100,000 astronomical units (AU) from the Sun, which is far beyond the reach of even the most powerful telescopes. The objects within the Oort Cloud are relatively small and dim, and are largely obscured by the vast distances and ambient light of the Milky Way galaxy. However, indirect evidence of the Oort Cloud can be seen in the form of long-period comets, which are believed to originate from the Oort Cloud and occasionally venture into the inner solar system where they can be observed from Earth.
Why is the Oort cloud important to astronomers
The Oort Cloud is important to astronomers for several reasons:
- Origin of comets: The Oort Cloud is believed to be the source of long-period comets that occasionally venture into the inner solar system. By studying these comets, astronomers can learn about the composition and structure of the Oort Cloud, as well as the early history of our solar system.
- History of the solar system: The objects within the Oort Cloud are thought to be remnants from the early days of our solar system, when the planets and other bodies were still forming. By studying the composition and orbits of these objects, astronomers can gain insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system.
- Search for life: Some scientists have suggested that the Oort Cloud may have been responsible for bringing water and other organic compounds to Earth during its early history, which could have played a crucial role in the development of life on our planet. By studying the composition and properties of objects within the Oort Cloud, astronomers may be able to identify other potential sources of life in the universe.
- Exploration: The Oort Cloud is a vast and largely unexplored region of space, which presents numerous opportunities for exploration and discovery. Proposed missions to explore the Oort Cloud could help to unlock the secrets of this enigmatic region, and provide valuable insights into the history and evolution of our solar system.
In summary, the Oort Cloud is an important area of study for astronomers, as it holds clues to the early history and evolution of our solar system, as well as the potential for discovering new sources of life and opportunities for exploration.