Unlocking the Cosmic Code: Exploring the Significance of Zodiac Constellations
Introduction
The night sky has been a source of fascination and wonder for humanity throughout history. Among the many celestial wonders that have captivated our imaginations, the zodiac constellations hold a special place. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of the zodiac, exploring what it is and why these constellations have been so significant in cultures around the world.
The Zodiac: A Brief Overview
What is the Zodiac?
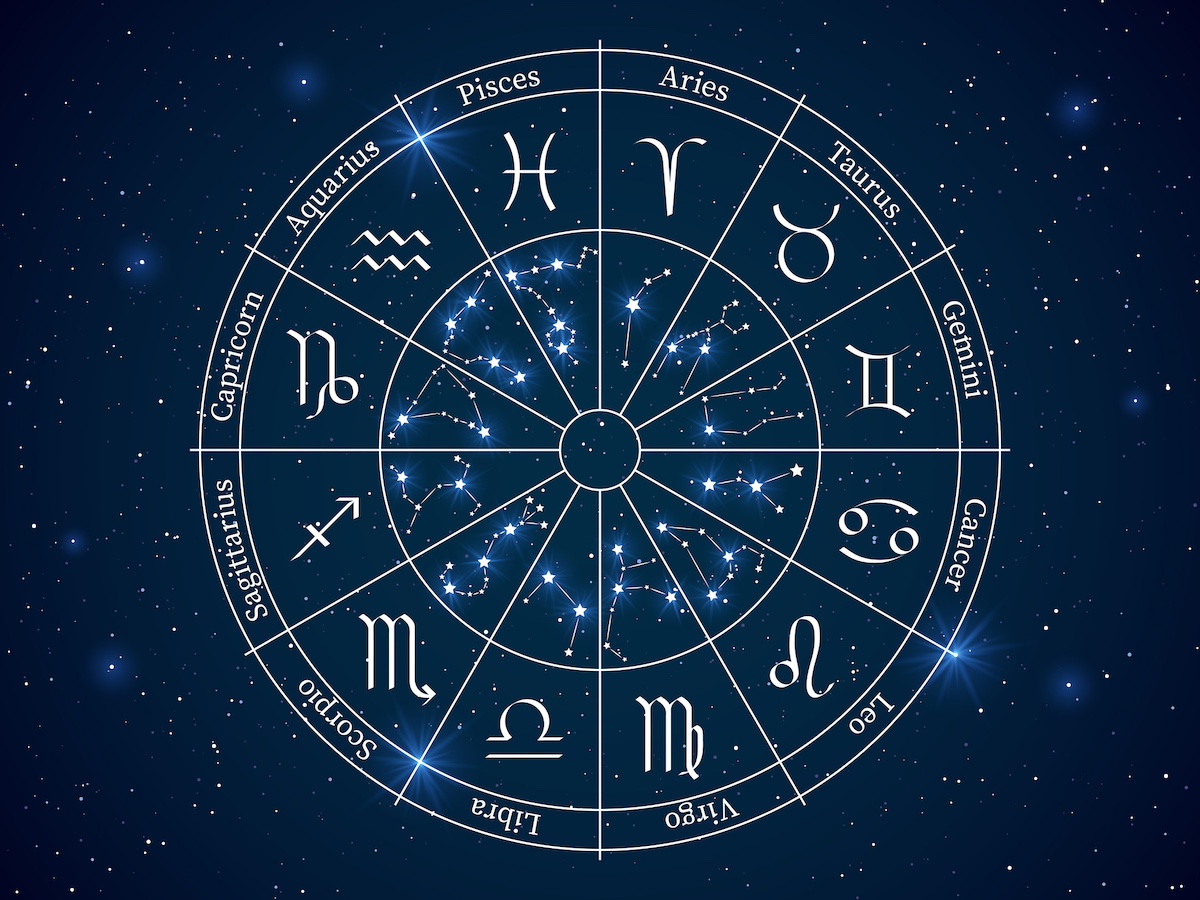
The term “zodiac” originates from the Greek word “zodiakos kyklos,” meaning “circle of animals.” It refers to a band or belt in the sky through which the sun, moon, and planets appear to move as they travel across the celestial sphere. This band is divided into 12 equal sections, each associated with a specific constellation – the zodiac constellations.
The Twelve Zodiac Constellations
The 12 zodiac constellations are: Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. These constellations have been used for millennia to understand and interpret celestial events and their potential influence on human life.
The Historical Significance of Zodiac Constellations
Early Observations and Interpretations
The study of the zodiac can be traced back to ancient civilizations, including the Babylonians, Egyptians, and Greeks. These cultures observed the patterns of stars in the night sky and developed myths and legends to explain the movements of celestial bodies within the zodiac.
The Babylonians, for example, are credited with creating the concept of the zodiac around 4000 years ago. They divided the zodiac into 12 equal parts, each corresponding to one of the zodiac constellations. This division was based on the position of the sun on the day a person was born, giving rise to the concept of astrological birth charts.
The Role of Astrology
Astrology, which is closely intertwined with the zodiac, is the belief that the positions and movements of celestial bodies can influence human behavior and destiny. It is important to note that astrology is considered a pseudoscience by the scientific community, but it has had a profound impact on culture and history.
Astrologers use the zodiac constellations to create horoscopes, which are personalized interpretations of an individual’s personality, strengths, weaknesses, and life events based on their birth date and the positions of celestial bodies at that time. While astrology’s scientific validity is highly debated, it continues to be popular and influential in many societies.
The Zodiac in Different Cultures
Chinese Zodiac
In addition to the Western zodiac, many cultures around the world have their own interpretations of the zodiac. One of the most well-known is the Chinese zodiac, which is based on a 12-year cycle associated with animal signs. Each year in the Chinese zodiac is linked to an animal, such as the Rat, Ox, Tiger, and so on. The Chinese zodiac is widely used in East Asian countries and plays a significant role in Chinese culture and traditions.
Indian Astrology
Indian astrology, also known as Vedic astrology, has its own system of zodiac signs, which are closely related to the positions of celestial bodies at the time of a person’s birth. Indian astrology places a strong emphasis on the influence of the moon and its 27 lunar constellations, known as Nakshatras, in addition to the 12 zodiac signs.
Mayan Zodiac
The ancient Maya civilization had its own zodiac system, which was based on the movement of celestial bodies and their relationship to earthly events. The Mayan zodiac included 20 different day signs, each with its unique characteristics and symbolism. This zodiac system played a vital role in Mayan astronomy and rituals.
Astronomy and the Zodiac
Astronomical Basis of the Zodiac
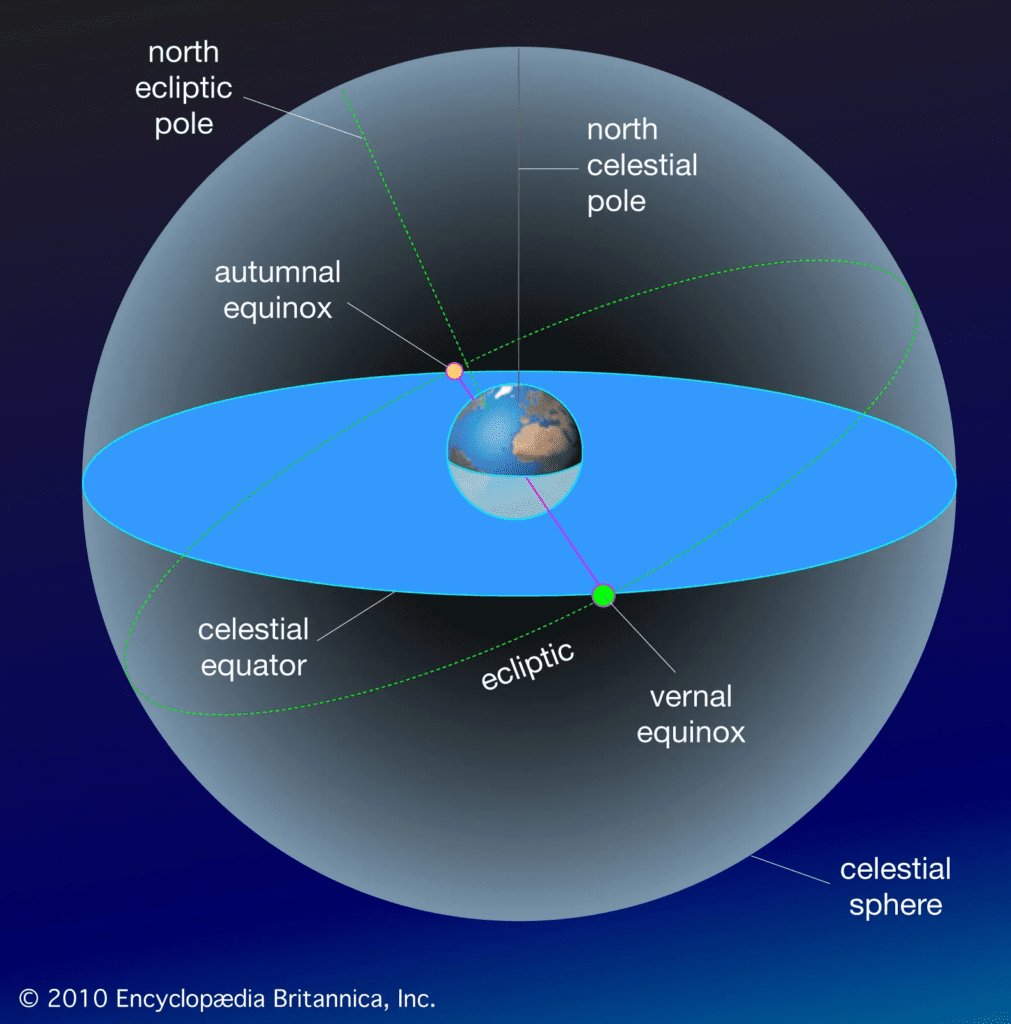
While the zodiac has strong cultural and astrological significance, it is important to understand its astronomical foundation. The zodiac constellations are, in fact, specific groups of stars located along the ecliptic, the apparent path that the sun traces across the sky over the course of a year. As the Earth orbits the sun, the sun appears to move through each of the 12 zodiac constellations.
Precession of the Equinoxes
One of the most intriguing aspects of the zodiac is the phenomenon known as the precession of the equinoxes. This slow, cyclical movement causes the position of the vernal equinox (the point at which the sun crosses the celestial equator) to shift gradually through the zodiac over a period of approximately 26,000 years. This means that the zodiac constellations we associate with specific astrological signs today may not align with the actual positions of the stars in the sky as they did in ancient times.
The Influence of the Zodiac in Modern Culture
Pop Culture and Entertainment
The zodiac and astrology continue to be prominent in modern culture, particularly in entertainment and media. Horoscopes are a regular feature in newspapers and magazines, providing readers with astrological insights and advice based on their zodiac sign. Additionally, many movies, television shows, and books incorporate astrology and zodiac themes into their narratives, further perpetuating the fascination with the zodiac.
Fashion and Design
The zodiac has also made its mark in the world of fashion and design. Many fashion designers and jewelry makers create pieces inspired by zodiac symbols and constellations. Zodiac-themed clothing, accessories, and home decor items are popular among those who want to express their astrological identity or simply appreciate the aesthetic appeal of the zodiac.
Scientific Perspective on the Zodiac
Astrology vs. Astronomy
While astrology and the zodiac have deep-rooted cultural significance, it is crucial to differentiate them from astronomy, the scientific study of celestial objects and phenomena. Astronomy does not support the claims made by astrology regarding the influence of celestial bodies on human behavior and destiny.
The positions of the stars in the zodiac constellations have changed over time due to the precession of the equinoxes, which undermines the accuracy of astrological predictions based on the constellations’ positions. Astronomers view astrology as a pseudoscience because it lacks empirical evidence and scientific validity.
The Zodiac and Personal Belief
Personal Interpretation and Belief
For many individuals, the zodiac holds personal significance as a form of self-exploration and reflection. While astrology may not be scientifically proven, some people find value in the introspective aspects of their astrological signs. They use horoscopes and astrological readings as a tool for self-discovery and personal growth, even if they do not subscribe to astrology’s predictive claims.
Psychological Aspect
Psychologists have explored the psychological aspects of belief in astrology. Some studies suggest that people who identify strongly with their astrological signs may exhibit confirmation bias, interpreting general astrological statements as personally meaningful. This phenomenon highlights the power of belief and its potential influence on individual behavior and attitudes.
Understanding Constellations
Defining Constellations
A constellation is a recognizable pattern of stars in the night sky, often representing a mythological character, creature, or object. These patterns are the product of human imagination and interpretation, as there are no physical connections between the stars within a constellation. Instead, they are simply stars that happen to appear in the same region of the sky when viewed from Earth.
Historical Significance
Constellations have played a vital role in the development of astronomy and human culture. Throughout history, various cultures have created their own constellations and associated them with legends, stories, and beliefs. These patterns served as celestial navigation aids, seasonal markers, and sources of inspiration for art, literature, and religion.
The Illusion of Proximity
The Perceived Closeness of Stars
One common misconception about constellations is that the stars within them are physically close to each other due to their apparent proximity in the night sky. However, this is a visual illusion caused by our perspective from Earth. In reality, the stars in a constellation can be vastly different in terms of distance from us and from each other.
The 3D Nature of Space
To better understand the true spatial relationships between stars in a constellation, it’s essential to grasp the three-dimensional nature of space. Stars are not spread evenly throughout the universe but are rather scattered at varying distances from Earth. Constellations are purely two-dimensional projections of these distant stars onto the celestial sphere.
Distance Disparities in Constellations
Proxima Centauri and Alpha Centauri
A classic example of the disparity in star distances within a constellation is the Alpha Centauri system. Alpha Centauri is part of the Centaurus constellation, and from Earth, it appears to be a single star. However, it is a triple star system consisting of three stars: Alpha Centauri A, Alpha Centauri B, and Proxima Centauri.
- Alpha Centauri A and B are Sun-like stars located approximately 4.37 light-years away from Earth, making them the closest known stars to our solar system.
- Proxima Centauri, while part of the same constellation, is significantly farther away at around 4.24 light-years.
The Big Dipper
Another well-known example is the Big Dipper, part of the Ursa Major constellation. This prominent asterism is often used for navigation and is composed of seven bright stars. However, these stars are not related in space. They vary in distance from Earth, with the closest being about 58 light-years away and the farthest over 120 light-years distant.
Constellations Across Cultures
Mythology and Cultural Variations
Different cultures have created their own constellations based on their unique mythologies and perspectives. For instance:
- The Greek constellation Orion, known for the mighty hunter in Greek mythology, is paralleled by other cultures with their own stories. The Lakota Sioux see it as the Hand constellation, representing a handprint, while in Australian Aboriginal astronomy, Orion is often associated with the Yeperenye, a man who travels across the sky.
- The Chinese constellation of the Dragon, which weaves its way through the northern sky, is associated with powerful and benevolent dragons in Chinese mythology. It differs significantly from Western dragon imagery.
- The Inca civilization in South America had their own constellations, such as the Llama, which represented the sacred animal, and the Serpent, symbolizing water and fertility.
Modern Astronomy and Constellations
Astronomical Organizations and Standardization
In modern astronomy, efforts have been made to standardize constellations and their boundaries. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) is the organization responsible for officially recognizing and defining constellations. Their work aims to establish a consistent set of constellations based on 88 designated regions of the sky, each with defined boundaries.
Deep-Sky Objects and Star Clusters
While constellations may be primarily associated with patterns formed by stars, they also contain deep-sky objects such as galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters. These objects are often observed within or near specific constellations and add to the richness of celestial exploration.
Zodiac Constellations
In this extensive exploration of the zodiac and its significance, we have journeyed through history, culture, and science. The zodiac, with its 12 constellations and rich mythological associations, has left an indelible mark on human civilization. While its astrological claims may remain contentious, the zodiac continues to inspire curiosity, self-reflection, and creativity in our modern world.
As you gaze up at the night sky, consider the enduring allure of the zodiac – a celestial tapestry that has connected humanity to the cosmos for millennia. Whether you view it through the lens of ancient wisdom, personal belief, or scientific skepticism, the zodiac remains a fascinating and enduring aspect of our shared human experience.
Don’t forget to check out these additional resources for more insights into the zodiac: