The Gaia Mission
The Gaia Mission, an extraordinary endeavor in the realm of astronomy, is an intricate dance between technology, curiosity, and human ingenuity. At its core, this mission is a testament to humanity’s relentless pursuit of understanding the cosmos. With precision and grace, Gaia aims to unravel the mysteries of our galaxy, offering unprecedented insights into its structure, evolution, and composition.
Gaia Mission: A Brief Overview
The Gaia Mission is a culmination of human ingenuity, technological innovation, and scientific ambition. Conceived and executed by the European Space Agency (ESA), it represents a milestone in our quest to understand the cosmos. Launched on December 19, 2013, aboard a Soyuz rocket from the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana, Gaia embarked on a journey unlike any other.
Visionary Objectives
The primary objective of the Gaia Mission is to chart a three-dimensional map of the Milky Way galaxy with unprecedented precision. Previous astronomical surveys provided glimpses of our galaxy’s structure, but Gaia seeks to revolutionize our understanding by cataloging over a billion stars with unparalleled accuracy. By measuring the positions, distances, motions, and properties of these stars, Gaia aims to create a celestial atlas that will serve as a cornerstone for astrophysical research for decades to come.
Cutting-Edge Instrumentation
At the heart of the Gaia spacecraft lies an array of sophisticated instruments designed to capture and analyze the light emitted by distant stars. Gaia’s two telescopes work in tandem to observe the sky, while its billion-pixel camera captures high-resolution images of celestial objects. These images are then processed and analyzed onboard the spacecraft before being transmitted back to Earth for further study. Gaia’s instruments are meticulously calibrated to ensure the accuracy of its measurements, allowing scientists to extract precise data from the vast cosmic tapestry.
Precision Measurements
One of the key innovations of the Gaia Mission is its ability to measure the positions and motions of stars with extraordinary accuracy. By observing each star multiple times over the course of its mission, Gaia can track their movements with unprecedented precision. This level of accuracy enables scientists to study the dynamics of our galaxy in exquisite detail, from the chaotic orbits of binary stars to the gentle drift of stellar clusters through space. Gaia’s measurements provide crucial insights into the gravitational forces that shape the Milky Way, shedding light on its past, present, and future evolution.
Data Processing and Analysis
The sheer volume of data generated by the Gaia Mission is staggering, requiring sophisticated algorithms and computational techniques to process and analyze. Gaia’s data processing pipeline is a marvel of modern engineering, capable of handling petabytes of information with efficiency and accuracy. Once processed, the data is made available to scientists around the world through the Gaia Data Archive, where it can be accessed and analyzed using a variety of tools and software. This open access approach fosters collaboration and innovation, allowing researchers to explore the cosmos in ways previously unimaginable.
Ongoing Mission
Since its launch, Gaia has exceeded all expectations, surpassing its original mission objectives and continuing to operate long beyond its planned lifespan. As of January 2024, Gaia has completed over 250 billion measurements, charting the positions and motions of more than 1.8 billion stars. With each passing day, Gaia continues to push the boundaries of our knowledge, uncovering new mysteries and revealing the hidden wonders of the universe. As the Gaia Mission enters its next phase, the journey of exploration and discovery continues, with countless new discoveries waiting to be made.
Mapping the Milky Way
Mapping the Milky Way is a monumental task that lies at the heart of the Gaia Mission’s objectives. Unlike terrestrial cartography, which involves charting the contours of Earth’s surface, mapping our galaxy requires a sophisticated understanding of celestial mechanics and a keen eye for detail. Through its meticulous observations and precision measurements, Gaia seeks to create a comprehensive three-dimensional map of the Milky Way, offering insights into its structure, composition, and evolution.
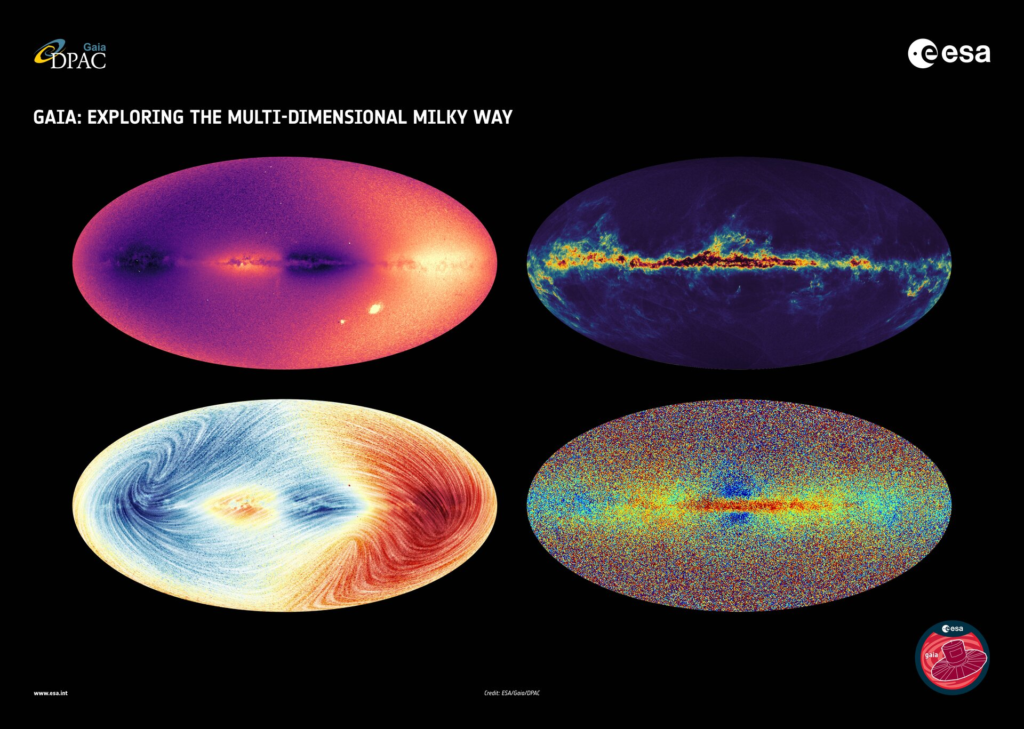
Unraveling the Galactic Tapestry
The Milky Way is a vast and intricate tapestry of stars, gas, and dust, woven together by the forces of gravity and stellar evolution. From the bustling center of the galaxy to the quiet suburbs of the outer disk, the Milky Way is home to billions of stars, each with its own unique story to tell. Gaia’s mission is to unravel this cosmic tapestry, charting the positions and motions of stars with unprecedented accuracy.
Precise Measurements
Central to Gaia’s mapping efforts is its ability to measure the positions and motions of stars with extraordinary precision. Using a technique known as astrometry, Gaia observes each star multiple times over the course of its mission, allowing scientists to track its movements with exquisite accuracy. By combining these measurements with data from other astronomical surveys, Gaia can create a detailed map of the Milky Way, revealing its structure and dynamics in unprecedented detail.
Galactic Coordinates
One of the challenges of mapping the Milky Way is defining a coordinate system that accurately represents its three-dimensional structure. Traditionally, astronomers have used a system known as galactic coordinates, which is based on the plane of the Milky Way and the position of the Sun. Gaia’s measurements provide crucial data points for refining these coordinates, allowing astronomers to map the galaxy with greater precision.
Galactic Features
As Gaia maps the Milky Way, it reveals a wealth of fascinating features, from dense star clusters to sprawling spiral arms. By analyzing the distribution of stars and their motions, astronomers can identify structures such as stellar streams, dwarf galaxies, and even dark matter halos. These features offer clues about the formation and evolution of the Milky Way, providing insights into its history and future destiny.
Beyond the Milky Way
While Gaia’s primary focus is on mapping the Milky Way, its observations also extend beyond our galaxy’s borders. By measuring the positions and motions of nearby galaxies, Gaia contributes to our understanding of the broader cosmic landscape. From the Magellanic Clouds to the Andromeda Galaxy, Gaia’s data provides valuable insights into the dynamics of galactic interactions and the larger structure of the universe.
A Continual Journey
Mapping the Milky Way is an ongoing process that evolves with each new observation and discovery. As Gaia continues its mission, it refines our understanding of our galaxy’s structure and dynamics, uncovering new mysteries and revealing hidden treasures along the way. With each passing day, Gaia brings us closer to unraveling the secrets of the Milky Way, illuminating the cosmic tapestry with unparalleled clarity and precision.
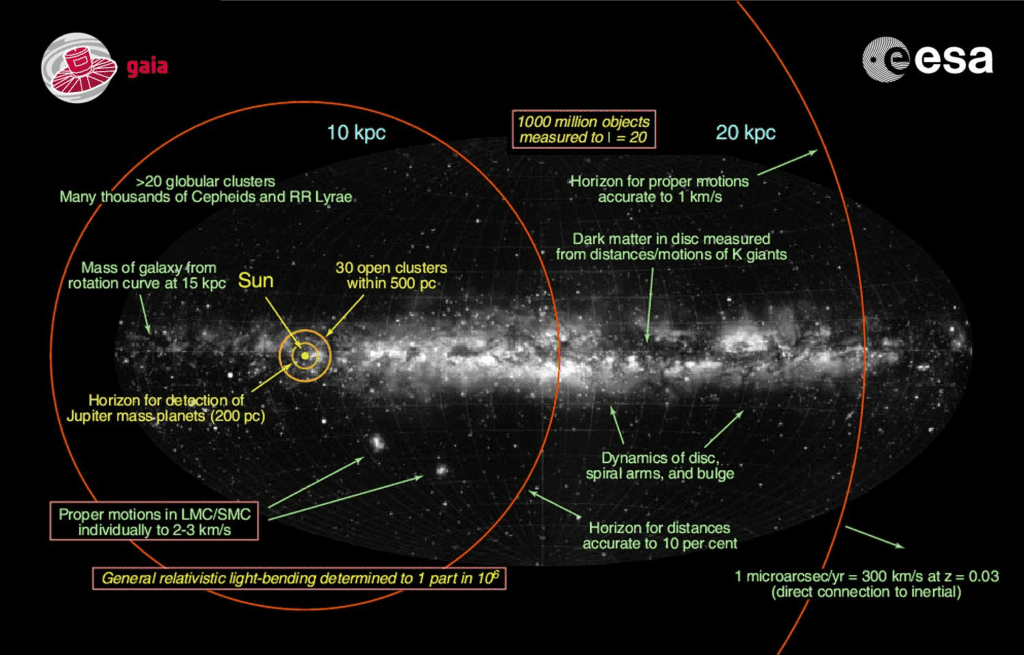
Unveiling Stellar Dynamics
Stellar dynamics, the study of how stars move and interact within galaxies, is a fundamental aspect of astrophysics. The Gaia Mission plays a pivotal role in unraveling the complex dance of celestial bodies within the Milky Way, offering unprecedented insights into stellar dynamics and their influence on the evolution of galaxies.
Gravitational Interactions
At the heart of stellar dynamics lie the gravitational interactions between stars. Like planets orbiting a star, stars within a galaxy are bound together by the force of gravity. Gaia’s precise measurements allow scientists to track the motions of stars as they orbit the galactic center, revealing the underlying gravitational forces at play. From binary star systems to massive stellar clusters, Gaia’s observations provide crucial data for understanding the dynamics of stellar systems on both small and large scales.
Galactic Orbits
One of the key questions in stellar dynamics is how stars move within the Milky Way. By observing the positions and velocities of stars, Gaia enables scientists to map out their orbits around the galactic center. These orbits can take various forms, from circular orbits within the galactic disk to elongated orbits that carry stars far above or below the plane of the galaxy. Gaia’s data allows astronomers to trace the paths of individual stars over time, shedding light on the overall structure and dynamics of the Milky Way.
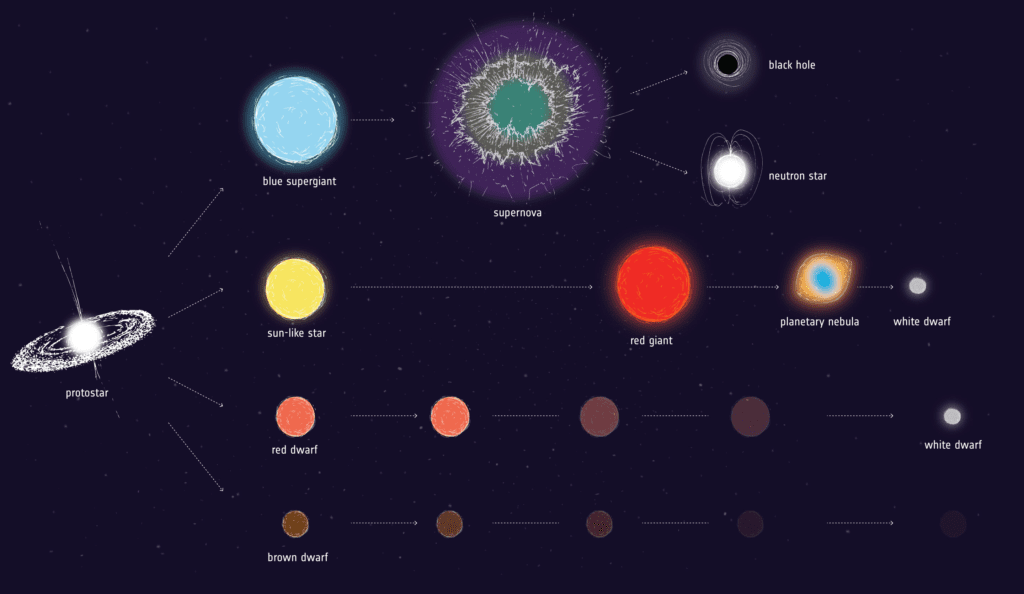
Stellar Populations
Another aspect of stellar dynamics is the study of stellar populations, groups of stars that share common characteristics such as age, composition, and spatial distribution. Gaia’s measurements provide valuable insights into the demographics of stars within the Milky Way, allowing astronomers to identify different stellar populations and study their properties in detail. By analyzing the motions and positions of stars, Gaia helps astronomers classify stellar populations and unravel their evolutionary histories.
Galactic Dynamics
Gaia’s observations also contribute to our understanding of the broader dynamics of the Milky Way galaxy. By measuring the motions of stars within the galactic disk, Gaia reveals the rotation of the Milky Way and the distribution of mass within its spiral arms. These measurements provide valuable constraints for models of galactic evolution, allowing astronomers to test theories about the formation and evolution of galaxies. Gaia’s data also allows astronomers to study the interactions between the Milky Way and its satellite galaxies, providing insights into the dynamics of galactic mergers and interactions.
Stellar Streams and Tidal Tails
One of the most intriguing aspects of Gaia’s observations is the discovery of stellar streams and tidal tails, faint trails of stars that trace the orbits of disrupted satellite galaxies or star clusters. These structures offer clues about the Milky Way’s turbulent history of galactic cannibalism, where smaller galaxies are torn apart by the gravitational forces of the larger Milky Way. Gaia’s precise measurements allow astronomers to identify and study these stellar streams in detail, providing insights into the dynamics of galactic accretion and the formation of the Milky Way’s halo.
Probing Galactic Archaeology
Galactic archaeology is a field of astrophysics that seeks to unravel the history of galaxies, including their formation, evolution, and composition, by studying the properties of their constituent stars. The Gaia Mission plays a pivotal role in this endeavor, providing astronomers with unprecedented insights into the Milky Way’s ancient past and its ongoing evolution.
Stellar Ages and Chemical Compositions
One of the key goals of galactic archaeology is to determine the ages and chemical compositions of stars within the Milky Way. By analyzing the light emitted by stars, astronomers can infer their ages and chemical abundances, providing clues about the conditions in which they formed. Gaia’s precise measurements allow scientists to determine the ages and chemical compositions of millions of stars across the galaxy, shedding light on its evolutionary history.
Stellar Populations
Galactic archaeologists classify stars into different populations based on their ages, chemical compositions, and spatial distributions within the galaxy. These populations provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of the Milky Way. Gaia’s measurements allow astronomers to identify and characterize different stellar populations, from ancient stars that formed shortly after the Big Bang to younger stars that are still in the process of formation.
Stellar Streams and Galactic Mergers
One of the most intriguing aspects of galactic archaeology is the study of stellar streams and tidal tails, faint trails of stars that trace the orbits of disrupted satellite galaxies or star clusters. These structures offer clues about the Milky Way’s turbulent history of galactic mergers and interactions. Gaia’s observations allow astronomers to identify and study these stellar streams in detail, providing insights into the dynamics of galactic accretion and the formation of the Milky Way’s halo.
Galactic Archaeological Surveys
In addition to Gaia’s observations, astronomers conduct targeted surveys to study specific regions of the Milky Way in more detail. These surveys use ground-based telescopes and spectroscopic instruments to measure the chemical compositions and kinematics of stars in different parts of the galaxy. By combining data from Gaia with observations from these surveys, astronomers can construct detailed maps of the Milky Way’s stellar populations and their properties.
Constraining Galactic Evolution
By probing the chemical compositions and ages of stars within the Milky Way, galactic archaeologists can constrain models of galactic evolution and formation. Gaia’s measurements provide valuable data points for testing theories about the origin and evolution of galaxies, including the Milky Way. By comparing observations with theoretical models, astronomers can refine our understanding of the processes that shaped the Milky Way over billions of years.
Revolutionizing Astrophysics
The Gaia Mission is not merely a scientific endeavor; it is a catalyst for innovation in astrophysics. Its unprecedented precision and scope have revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries in various fields. From exoplanet detection to gravitational wave astronomy, Gaia’s data serves as a cornerstone for countless research projects, pushing the boundaries of human knowledge.
The Gaia Data Catalog
Central to the success of the Gaia Mission is the creation of a comprehensive data catalog, freely accessible to scientists and the public alike. This treasure trove of information contains a wealth of data on billions of stars, including their positions, distances, motions, and properties. With user-friendly interfaces and powerful analysis tools, the Gaia Data Catalog empowers researchers to explore the cosmos in unprecedented detail.
Collaborative Endeavors
The impact of the Gaia Mission extends far beyond the boundaries of ESA. Collaborative efforts between international space agencies, research institutions, and individual scientists have been instrumental in maximizing the scientific output of Gaia’s data. Through shared resources and collective expertise, the global astronomical community continues to unlock the secrets of the universe, united by a common passion for discovery.
Looking to the Future
As the Gaia Mission enters its next phase, the journey of exploration and discovery continues. With ongoing observations and data releases, Gaia will continue to refine our understanding of the Milky Way and beyond. From unraveling the mysteries of dark matter to probing the dynamics of galactic collisions, the possibilities are endless. With each new revelation, Gaia reminds us of the boundless wonders that await us in the cosmos.
The Gaia Mission
The Gaia Mission stands as a testament to humanity’s insatiable curiosity and relentless pursuit of knowledge. Through its precision measurements and groundbreaking discoveries, Gaia has revolutionized our understanding of the Milky Way and reshaped the landscape of astrophysics. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of the universe, Gaia serves as a guiding light, illuminating the path towards new horizons of discovery and exploration.
References:

