The universe is vast and filled with countless celestial bodies, each with their own unique properties and characteristics. Astronomers use a variety of techniques to study these objects, allowing us to learn more about the universe and our place within it. In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the different types of astronomical bodies and the techniques used to study them.
Stars
Stars are perhaps the most well-known and easily recognizable celestial bodies in the universe. They are massive, luminous spheres of plasma held together by their own gravity. Stars come in many different sizes, colours, and stages of development. Some stars, like our sun, are considered main sequence stars and will burn hydrogen for billions of years before eventually running out of fuel. Others, like red giants or white dwarfs, are in later stages of their lives.
Astronomers study stars using a variety of techniques, including spectroscopy and photometry. Spectroscopy involves analysing the light emitted by a star to determine its composition, temperature, and other properties. Photometry, on the other hand, involves measuring the brightness of a star over time to learn about its variability and behaviour.
Galaxies
Galaxies are massive systems of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity. There are many different types of galaxies, including spiral galaxies like our own Milky Way, elliptical galaxies, and irregular galaxies. Galaxies can be millions or billions of light-years away from us, making them some of the most distant objects in the universe.
By analysing the light emitted by galaxies, astronomers can learn about their composition, age, and structure. Imaging techniques allow us to create detailed maps of galaxies, revealing their intricate structures and the motions of the stars and gas within them.
Planets
Planets are objects that orbit a star and are large enough to be spherical in shape. There are eight planets in our solar system, but astronomers have discovered thousands of exoplanets orbiting other stars in the galaxy. Each planet has its own unique properties, such as its size, composition, and distance from its star.
Direct imaging allows us to see the planet directly, revealing its size, colour, and other properties.
Other Celestial Bodies
The universe is full of other types of celestial bodies, such as comets, asteroids, and black holes. Comets are icy objects that originate from the outer reaches of the solar system, while asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the sun. Black holes are incredibly dense objects that warp space and time around them, making them some of the most fascinating objects
Astrophotography: Capturing the Beauty of the Night Sky
Astrophotography is a specialised type of photography that involves capturing images of celestial objects such as stars, galaxies, and nebulae. With the right equipment and techniques, astrophotographers can produce stunning images that showcase the beauty of the night sky.
Equipment
To capture high-quality astrophotography images, specialised equipment is needed. The most essential piece of equipment is a camera that is capable of capturing long-exposure shots. DSLR cameras are a popular choice among astrophotographers due to their ability to capture high-quality images and control settings such as exposure time and ISO.
In addition to a camera, a stable tripod or equatorial mount is also necessary to keep the camera steady during long exposures. A telescope or telephoto lens can also be used to magnify celestial objects and capture greater detail.
Techniques
One of the most important techniques in astrophotography is capturing long exposures. This involves leaving the shutter open for extended periods of time, ranging from a few seconds to several hours, to allow enough light to enter the camera and capture faint celestial objects.
Another important technique is image stacking, which involves combining multiple images of the same celestial object to increase the overall quality and reduce noise. This can be done manually or with specialised software designed for astrophotography.
Post-processing
After capturing the images, post-processing is necessary to bring out the best in the images. This can involve adjusting settings such as brightness, contrast, and colour balance, as well as removing any unwanted noise or artefacts.
Popular Subjects
There are many different subjects that astrophotographers can capture, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges. Some popular subjects include:
- Stars: Capturing images of individual stars or constellations can be a great way to showcase the beauty of the night sky.
- Nebulae: Nebulae are clouds of gas and dust that emit their own light and can create stunning images when captured in long exposures.
- Galaxies: Capturing images of galaxies can be a great challenge due to their distance and faintness, but the results can be truly breathtaking.
- Planets: While more challenging to capture due to their smaller size and faster movement across the sky, images of planets such as Jupiter and Saturn can reveal incredible detail and beauty.
In conclusion, astrophotography is a unique and rewarding hobby that allows photographers to capture the beauty of the night sky. With the right equipment and techniques, anyone can capture stunning images of celestial objects and share them with the world.
Planetary and Lunar Astronomy: Exploring Our Cosmic Neighbors
Planetary and lunar astronomy is the study of the celestial bodies in our solar system, including the planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. It is a fascinating field that allows us to explore our cosmic neighbours and learn more about the formation and evolution of our solar system.
Planetary Astronomy
Planetary astronomy is the study of the planets in our solar system, including their orbits, physical characteristics, and behaviour. There are eight planets in our solar system, each with its own unique properties and characteristics.
One of the most important techniques used in planetary astronomy is spectroscopy, which involves analysing the light emitted or reflected by a planet to determine its composition and properties. Spectroscopy can reveal information about the gases and minerals present in the planet’s atmosphere or surface, and can even detect the presence of water or other organic compounds.
Another important technique used in planetary astronomy is imaging, which allows us to capture detailed images of the surface features of a planet. This can be done using ground-based telescopes or spacecraft, such as the Mars rovers or the Cassini spacecraft that orbited Saturn.
Lunar Astronomy
Lunar astronomy is the study of our own moon, including its physical characteristics, behaviour, and history. The moon is the closest celestial body to Earth and has been studied extensively by astronomers and space agencies such as NASA.
One of the most important techniques used in lunar astronomy is photometry, which involves measuring the brightness of the moon over time. This can reveal information about the moon’s surface features, such as craters, mountains, and valleys, and can even detect the presence of volatile substances such as water ice.
Another important technique used in lunar astronomy is radar imaging, which allows us to map the subsurface features of the moon. This can reveal information about the moon’s internal structure and history, such as the presence of lava tubes or buried impact craters.
The Importance of Planetary and Lunar Astronomy
Studying the planets and moon in our solar system is important for many reasons. It can help us understand the formation and evolution of our solar system, as well as the potential for life on other planets and moons. It can also provide valuable information for future space exploration missions, such as identifying potential landing sites or resources that could be used for human exploration.
In conclusion, planetary and lunar astronomy is a fascinating field that allows us to explore the celestial bodies in our solar system and learn more about our cosmic neighbors. With the use of advanced techniques and technologies, we continue to make new discoveries and expand our understanding of the universe.
Observing deep sky objects
Observing Deep Sky Objects: A Guide to Exploring the Universe Beyond Our Solar System
Deep sky objects are celestial bodies that are located outside of our solar system, including galaxies, nebulae, star clusters, and other types of celestial objects. Observing deep sky objects can be a rewarding and fascinating hobby for amateur astronomers, allowing them to explore the vast universe beyond our solar system.
Equipment
To observe deep sky objects, you will need a telescope with a large aperture and a high-quality eyepiece. The larger the aperture of the telescope, the more light it can gather, allowing you to see fainter objects in the sky. A high-quality eyepiece is also important for producing clear and sharp images.
A stable mount is also important for keeping the telescope steady during observations. This can be a simple tripod or a more advanced equatorial mount that allows for tracking of celestial objects as they move across the sky.
Techniques
Observing deep sky objects requires patience and practice, as these objects are often faint and difficult to see. The following techniques can help you make the most of your observations:
- Dark Adaptation: Before observing deep sky objects, it is important to let your eyes adjust to the dark. This can take up to 30 minutes, so be patient and avoid looking at bright lights or screens during this time.
- Use Averted Vision: Averted vision involves looking slightly to the side of the object you are trying to observe, rather than directly at it. This can help you see fainter details and increase your chances of spotting the object.
- Filters: Specialised filters can be used to enhance the contrast and details of deep sky objects. For example, a narrowband filter can help isolate the light emitted by specific gases in a nebula, while a light pollution filter can reduce the effects of light pollution in urban areas.
Popular Deep Sky Objects
There are many different types of deep sky objects that can be observed with a telescope, each with its own unique properties and characteristics. Some popular deep sky objects include:
- Galaxies: There are billions of galaxies in the universe, ranging in size from small dwarf galaxies to massive spiral galaxies like our Milky Way. Galaxies can be observed as faint, fuzzy patches of light in the sky.
- Nebulae: Nebulae are clouds of gas and dust that emit their own light, creating stunning and colourful images. Some popular nebulae include the Orion Nebula and the Ring Nebula.
- Star Clusters: Star clusters are groups of stars that are held together by gravity. They can be observed as tight groups of stars in the sky, ranging from open clusters with a few dozen stars to globular clusters with hundreds of thousands of stars.
In conclusion, observing deep sky objects can be a rewarding and fascinating hobby for amateur astronomers. With the right equipment and techniques, anyone can explore the vast universe beyond our solar system and discover the wonders of the deep sky.
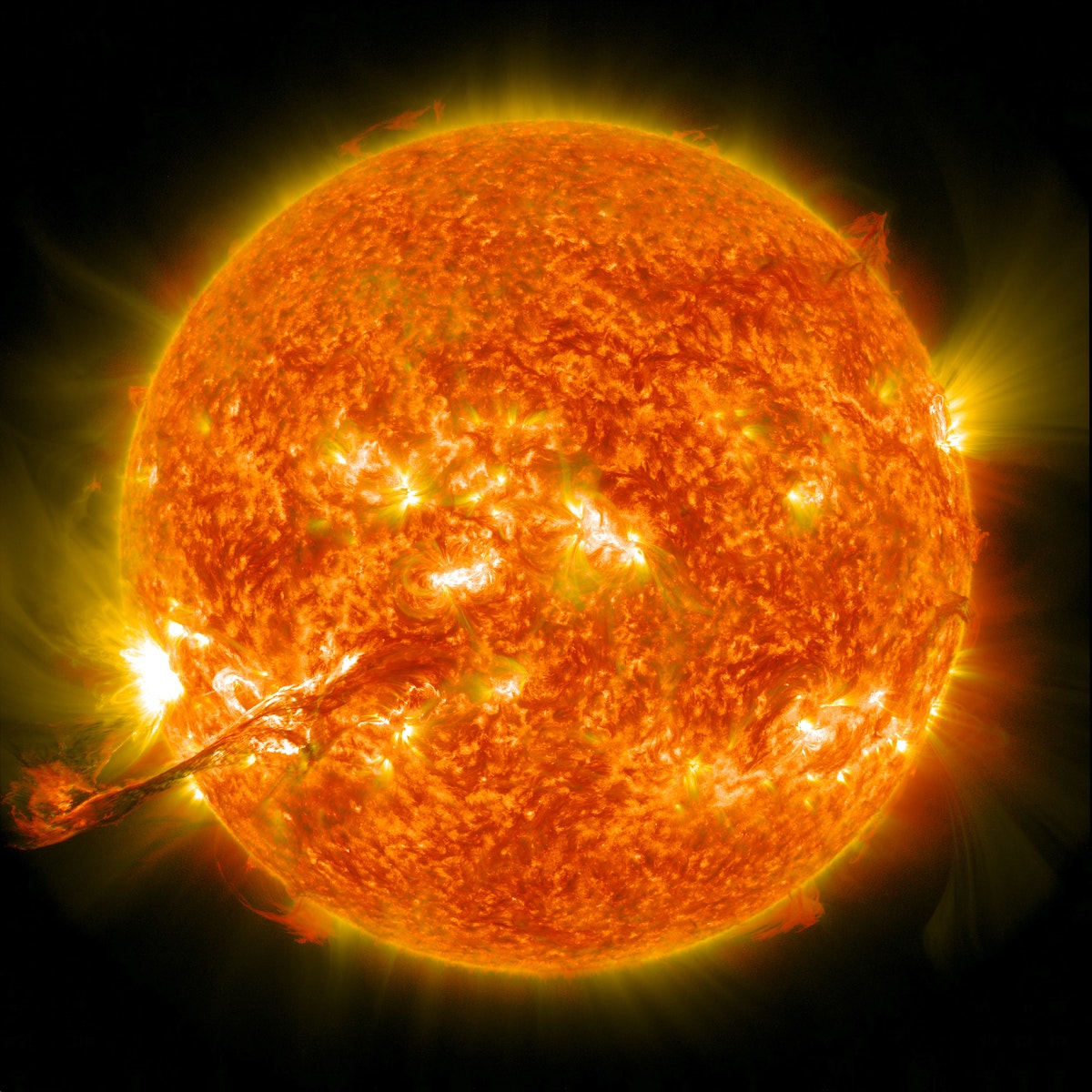
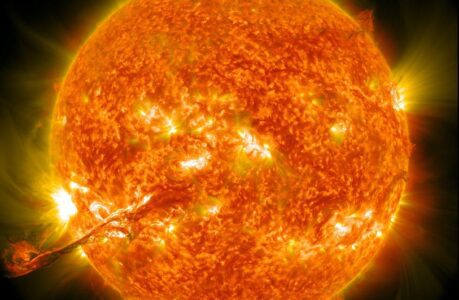
Solar Astronomy: Studying the Sun and its Effects on Earth
Solar astronomy is the study of the sun and its behaviour, including sunspots, solar flares, and other phenomena. The sun is a vital part of our solar system, providing light, heat, and energy that sustains life on Earth. Understanding the behaviour of the sun is important for predicting and mitigating the effects of solar activity on our planet.
Equipment
To study the sun, specialised equipment is needed to protect the eyes and capture images of the solar surface. The most important piece of equipment is a solar filter, which blocks harmful UV and IR radiation and allows safe observation of the sun. This can be a specialised solar telescope or a filter that is placed over a regular telescope or binoculars.
Another important piece of equipment for solar astronomy is a solar spectroscope, which allows scientists to analyse the spectrum of light emitted by the sun and learn more about its composition and behaviour.
Techniques
Solar astronomers use a variety of techniques to study the sun, including:
- Sunspot Observation: Sunspots are dark areas on the surface of the sun that are caused by magnetic activity. Observing sunspots can provide information about the behaviour of the sun’s magnetic field and can help predict solar flares and other phenomena.
- Solar Flare Observation: Solar flares are eruptions of energy on the sun’s surface that can have a wide range of effects on Earth, including radio interference and power outages. Observing and predicting solar flares is an important area of research in solar astronomy.
- Solar Spectroscopy: Solar spectroscopy involves analysing the spectrum of light emitted by the sun to learn more about its composition and behaviour. This can reveal information about the temperature, density, and motion of the sun’s outer layers.
The Importance of Solar Astronomy
Studying the sun is important for many reasons. Solar activity can have a wide range of effects on Earth, including changes in weather patterns, radio interference, and power outages. Understanding and predicting solar activity is important for mitigating the effects of these phenomena and protecting critical infrastructure such as satellites and power grids.
In addition, studying the sun can provide insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system, as well as the behaviour of other stars in the universe.
In conclusion, solar astronomy is a fascinating field that allows us to study the behaviour of our nearest star and its effects on our planet. With the right equipment and techniques, scientists and amateur astronomers alike can explore the mysteries of the sun and learn more about the universe around us.