Astronomy is a branch of science that has captured human imagination for centuries. The study of celestial bodies and their movements has been a crucial part of human culture and has led to some of the most significant discoveries in science. From the earliest civilisations to the present day, the history of astronomy is a story of human curiosity, discovery, and progress.
The earliest civilisations, such as the Babylonians and the Egyptians, used astronomy to track the movement of the stars and the planets, which they believed influenced the fate of the world. The Babylonians were the first to develop a systematic approach to astronomy and recorded the positions of celestial bodies in their famous astronomical diaries. Meanwhile, the Egyptians used astronomical observations to help with the timing of their agricultural activities, as well as to keep track of the movement of the Sun, Moon, and the stars.
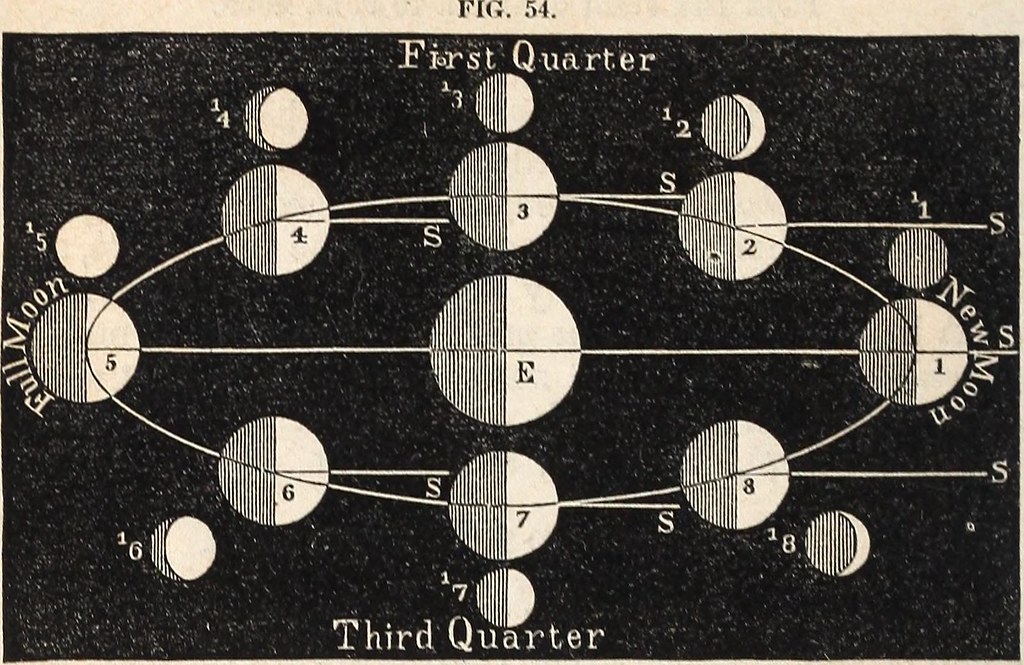
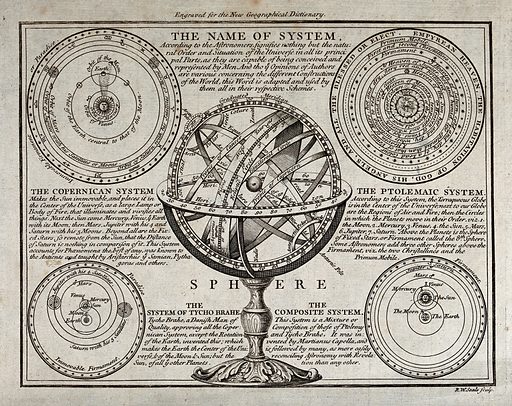
One of the most important moments in the history of astronomy was the development of the heliocentric model of the universe by the Greek philosopher Aristarchus in the 3rd century BCE. He proposed that the Earth and the other planets revolved around the Sun, which was a revolutionary idea at the time. The idea was later refined by the astronomer Ptolemy, who produced a comprehensive treatise on astronomy, the Almagest, which became the standard textbook for astronomers for over a thousand years.
In the 16th century, the invention of the telescope by Galileo Galilei revolutionised astronomy. He was the first person to observe the night sky with a telescope and made many important observations, including the discovery of four of Jupiter’s moons and the phases of Venus. His observations provided crucial evidence for the Copernican model of the solar system and helped to establish the idea that the Earth was not the centre of the universe.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, astronomical observation became increasingly sophisticated, and the development of photography and spectroscopy opened up new avenues of research. Astronomers were able to study the spectrum of light from stars, which revealed their composition and temperatures, and discovered the presence of elements like hydrogen and helium in the universe. The discovery of cosmic radiation by astronomers such as Robert Millikan and Arthur Compton helped to establish the Big Bang theory, which explained the origin of the universe.
The 20th century saw the development of space-based astronomy, which has allowed astronomers to study celestial objects in greater detail than ever before. The launch of the Hubble Space Telescope in 1990 was a major milestone in the history of astronomy, and its observations have provided scientists with new insights into the universe and its evolution. The discovery of exoplanets, or planets orbiting stars outside our solar system, has opened up the possibility of finding life elsewhere in the universe.
Today, the field of astronomy continues to evolve, with new telescopes and space missions planned for the future. The study of the sky has come a long way since the days of the earliest civilizations, and it is exciting to think about what new discoveries the future will bring.

